Three Node List
Now let us build a linked list with three nodes. This will be done with an eye to generalizing the procedure so that lists with any number of nodes can be built. Here is the picture:
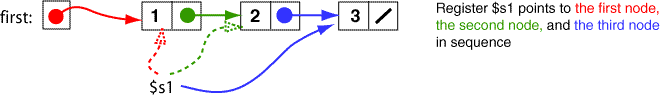
Let us first look at creating the first node. This is the same as before:
main:
# create the first node
li $v0,9 # allocate memory
li $a0,8 # 8 bytes
syscall # $v0 <-- address
move $s1,$v0 # $s1 = first node
# copy the pointer to first
sw ___,_____
# initialize the first node
li $t0,1 # store 1
sw $t0,0(___) # at displacement 0