The Exponent
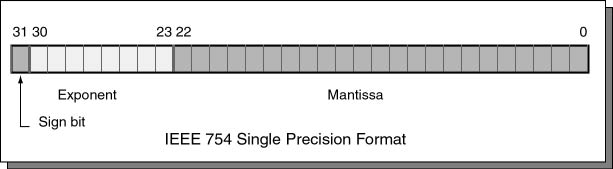
The eight bits 23 through 30 contain the exponent. The exponent is an integer, but may be negative, zero, or positive. You might guess that an 8-bit two's complement integer would work perfectly for this, but a different type of notation is used.
The exponent is expressed using a biased integer.
This is an unsigned binary integer that has +127
added to it.
- A biased exponent of
+127represents the actual exponent 0. - A biased exponent of
+128represents the actual exponent 1. - A biased exponent of
+126represents the actual exponent -1.
Exceptions: (1) when the entire float is zero
the exponent 0 is used.
(2) the exponent 255 is used
to signal various problems,
such as division by zero.