Complete Program
The base register is "moved" through the string by increasing the address by one for each byte. This is also called "moving a pointer". This program has an important concept on every line. Using these concepts is how you program!
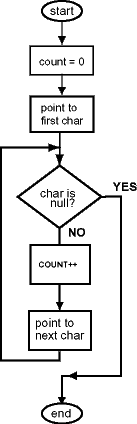
## strlen.asm
##
## Count the characters in a string
##
## Registers:
## $8 --- count
## $9 --- pointer to the char
## $10 --- the char (in low order byte)
.text
.globl main
# Initialize
main: ori $8,$0,0 # count = 0
lui $9,0x1000 # point at first char
# while not ch==null do
loop: lbu $10,0($9) # get the char
sll $0,$0,0 # branch delay
beq $10,$0,done # exit loop if char == null
sll $0,$0,0 # branch delay
addiu $8,$8,1 # count++
addiu $9,$9,1 # point at the next char
j loop
# finish
done: sll $0,$0,0 # target for branch
.data
string: .asciiz "Time is the ghost of space."
## End of file
The program is very close to the C standard library function
int strlen(char*).
As it is written, the program has its
own data,
and it is not written as a callable function.
We will do both of those things in a few chapters.