Model Summary
Here is a summary of the basic MIPS programming model. Click on the hyperlinks for more details.
Machine Instructions: Machine instructions are thirty-two bits wide. Bit patterns specify the operation, the operands, and the destination for the result. Basic operations are arithmetic, logic, memory access, and control branches.
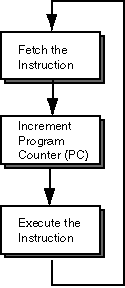
Machine Cycle: The machine cycle is illustrated at right. Execution proceeds sequentially one instruction at a time. The control point indicates the instruction about to execute. ALU operations never directly access memory.
Registers: Thirty-two 32-bit wide general purpose registers, which have various conventional uses. Register $0 is hard-wired to 32 zero-bits.
Memory: Thirty-two bit address space, but only the lower half (most of it anyway) is for user programs. User memory is further divided (by software convention) into text, data, and stack segments.
 Go to Table of Contents
Go to Table of Contents